Coefficient of determination is an evaluation metric based on the mean of the squared error. Higher values indicate better accuracy, up to a maximum value of 1.0.
Although the evaluation values described above are intuitive, they are affected by the size of the prediction value in the dataset.
For example, a price prediction for real estate has an error ratio of about seven digits (millions), whereas a prediction for incoming calls has an error ratio of about two digits (tens). Then, it becomes impossible to compare the accuracy of the real estate price prediction with the accuracy of the incoming call prediction.
Coefficient of determination is an evaluation metric that is not affected by the size or variability of the prediction values in the dataset (Real estate prices and incoming calls). Intuitive comprehension is difficult, but it is calculated as follows:
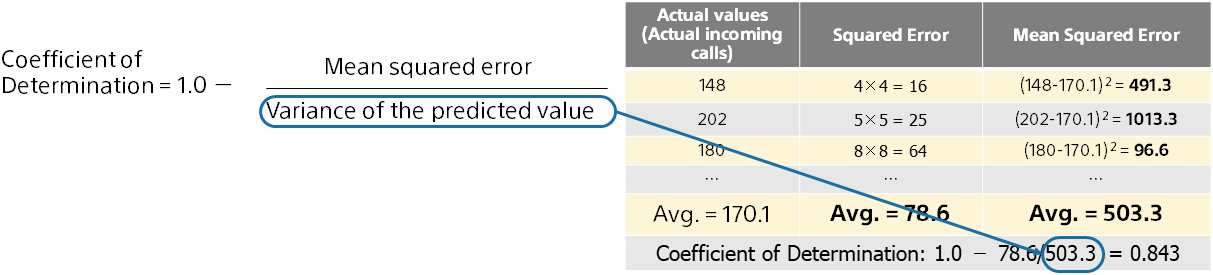
*“Variance” is one of the aggregate values of numeric values (statistics) and indicates the magnitude and variation of multiple numeric values. The average of the squares of the differences between each number.